Tuberculosis (TB)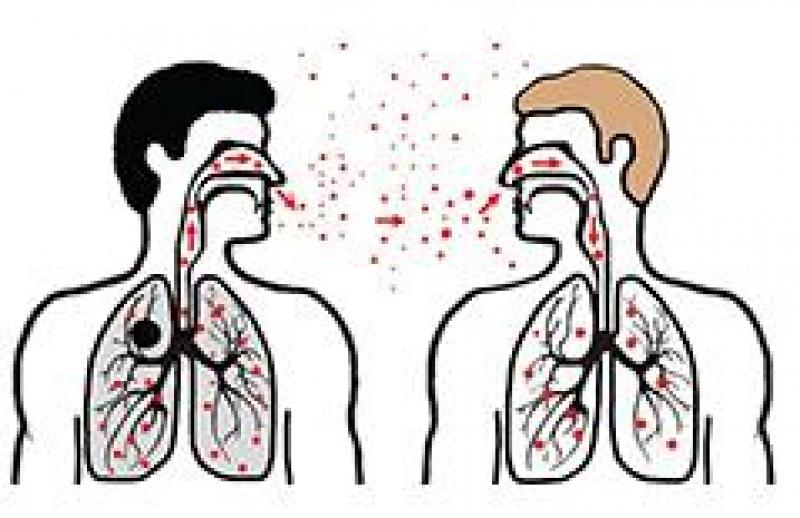
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial disease that most often affects the lungs. This is called pulmonary TB and can spread from person to person. However, TB can affect other parts of the body such as lymph nodes, kidneys, bone and joints. This is called extra-pulmonary (outside the lungs) disease.
Latent TB infection
When a person has latent TB infection they have TB bacteria in their body but are not sick with TB disease. They are not infectious and cannot spread TB. A person with latent TB infection can take antibiotics to kill the TB germs before they develop TB disease.
TB Disease
When the TB germ becomes active in a person’s body they develop TB disease. People with TB disease are sick and are able to spread the bacteria to other people. People with TB disease must be treated for 6-9 months with antibiotics. They also must isolate themselves to prevent spreading the disease until the antibiotics have taken affect.
Symptoms of TB disease include:
• a bad cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer
• pain in the chest
• coughing up blood or sputum
• weakness or fatigue
• weight loss, poor appetite
• chills, fever
• sweating at night
Testing for TB infection and Disease
There are two kinds of tests that are used to detect TB bacteria in the body: the TB skin test (TST) and TB blood tests. If you have a positive reaction to either of the tests, and do not have symptoms of TB disease you have latent TB infection. If you have a positive reaction and have TB symptoms you may have TB disease.
If your doctor does not offer testing, call 518-565-4848 to schedule an appointment.
Reviewed 11/30/2023


































